Memory overclocking can unlock significant performance gains for your system, going beyond the automatic profiles that come with your RAM. While XMP (Intel) and EXPO (AMD) profiles provide easy one-click overclocking, manual tuning can extract even more performance from your memory modules.
Understanding Memory Profiles
When you purchase DDR4 or DDR5 RAM, the advertised speeds rely on overclocking profiles. Without XMP or EXPO enabled, DDR4 runs at 3200 MT/s and DDR5 at 4800 MT/s – their official JEDEC specifications. The higher speeds marketed (sometimes exceeding 8000 MT/s for DDR5) require these profiles to be active in your BIOS.
These automatic profiles work by applying manufacturer-tested settings for speed, voltage, and timings. However, there’s often room for further optimization through manual tuning.
1. Know Your Memory Modules
Before diving into manual overclocking, research your specific RAM thoroughly. Check the physical labels on your modules and look up the model numbers online. Manufacturer specifications, reviews, and overclocking guides for your exact model provide valuable baseline information.
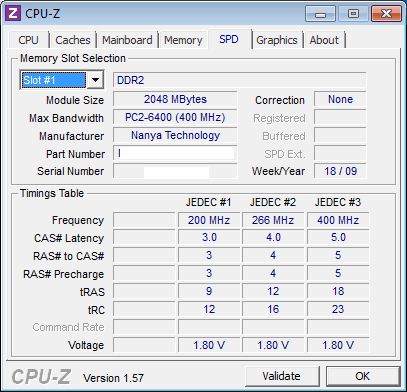
Key considerations:
- Use identical modules for best results (same brand, model, speed, and timings)
- Never mix different RAM kits, even with similar specifications
- Every memory chip is unique due to manufacturing variations
- Results will vary even between identical systems
Understanding these limitations helps set realistic expectations and prevents frustration during the tuning process.
2. Take Incremental Steps
Approach memory overclocking methodically, making small adjustments between tests. Start with your baseline XMP/EXPO settings and gradually increase one parameter at a time.
Progressive approach:
- Begin with automatic profile settings to establish baseline performance
- Make single-parameter changes (speed OR voltage OR timings)
- Test stability before proceeding to the next adjustment
- Document successful configurations for reference
This methodical approach helps identify which specific changes cause instability. Changing multiple parameters simultaneously makes troubleshooting difficult when problems arise.
3. Validate Every Change
System boot success doesn’t guarantee stability under load. Memory errors often appear only during intensive operations, making thorough testing essential.
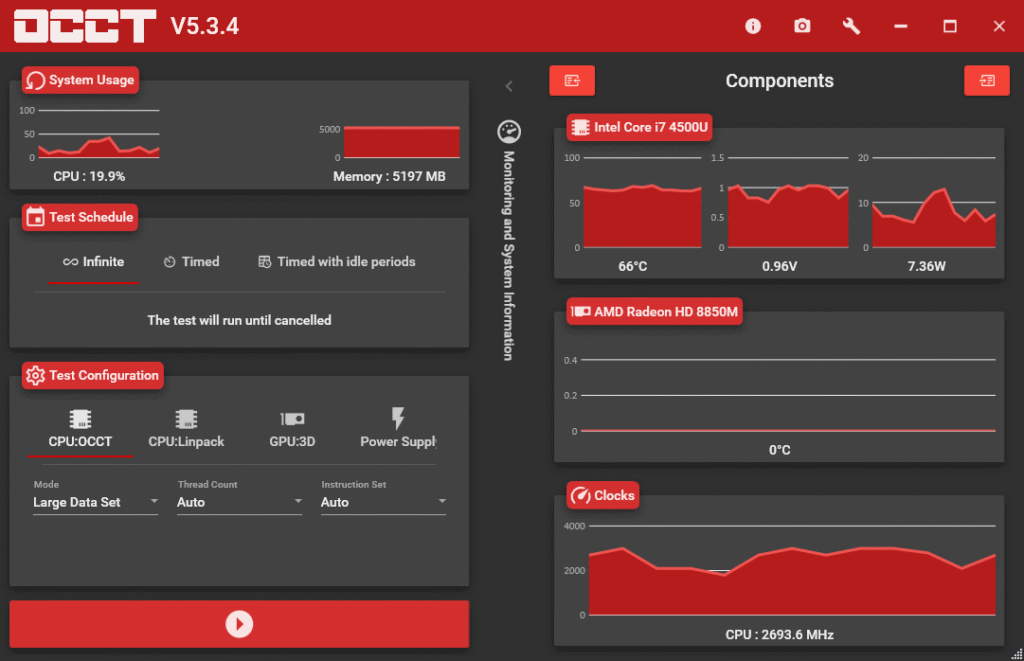
Testing methodology:
- Run stress tests after each adjustment
- Use tools like MemTest86 for comprehensive memory validation
- Consider OCCT for detailed analysis of timings and bandwidth
- Test for several hours, not just minutes
- Monitor for system crashes, blue screens, or data corruption
If instability occurs, reduce the last change slightly and retest. This iterative process ensures reliable daily operation.
4. Leverage Motherboard Tools
Modern motherboards offer sophisticated memory tuning utilities that simplify the overclocking process. These tools can automatically suggest safe settings and provide real-time monitoring.
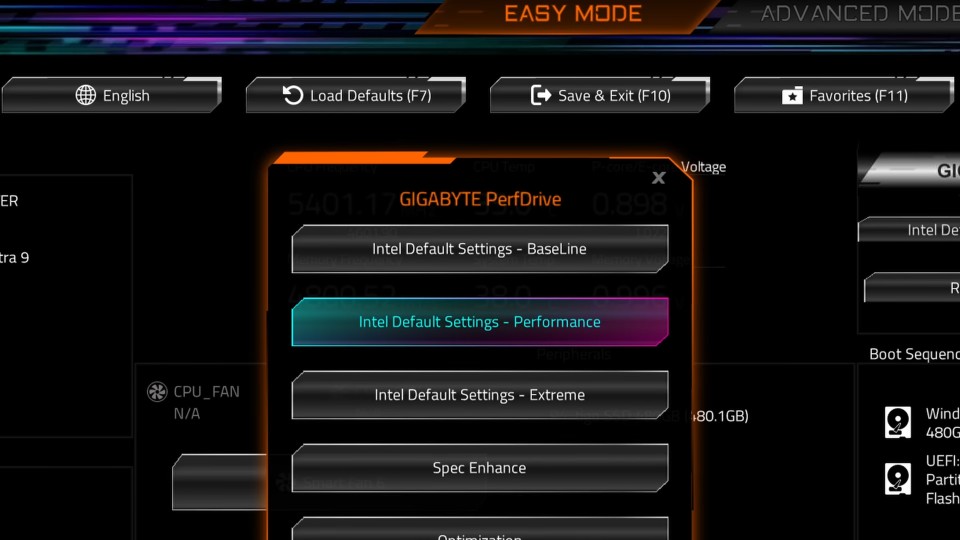
Motherboard features to utilize:
- Built-in memory training algorithms
- Automatic timing calculators
- Voltage recommendation systems
- Real-time stability monitoring
- Preset overclocking profiles beyond XMP/EXPO
Many motherboards also include memory topology information, helping optimize settings for your specific configuration.
Performance Benefits
Properly tuned memory can provide:
- Improved gaming frame rates
- Faster application loading times
- Better multitasking performance
- Enhanced productivity in memory-intensive tasks
The performance gains are often most noticeable in CPU-bound scenarios and applications that benefit from increased memory bandwidth.

Safety Considerations
While memory overclocking is generally safe, follow these precautions:
- Never exceed manufacturer voltage recommendations
- Monitor temperatures during stress testing
- Keep backup BIOS settings or know how to clear CMOS
- Start with conservative settings and work upward
- Accept that not all modules can achieve extreme overclocks
Remember that stability should always take priority over maximum performance. A system that crashes randomly is worse than one running at slightly lower speeds reliably.
Conclusion
Manual memory tuning offers performance improvements beyond automatic XMP and EXPO profiles, but requires patience and systematic testing. By understanding your hardware, making incremental changes, validating stability, and using available tools, you can safely unlock additional performance from your memory investment.
The key to successful memory overclocking lies in careful methodology rather than aggressive settings. Take your time, document your progress, and prioritize stability over peak numbers for the best long-term results.